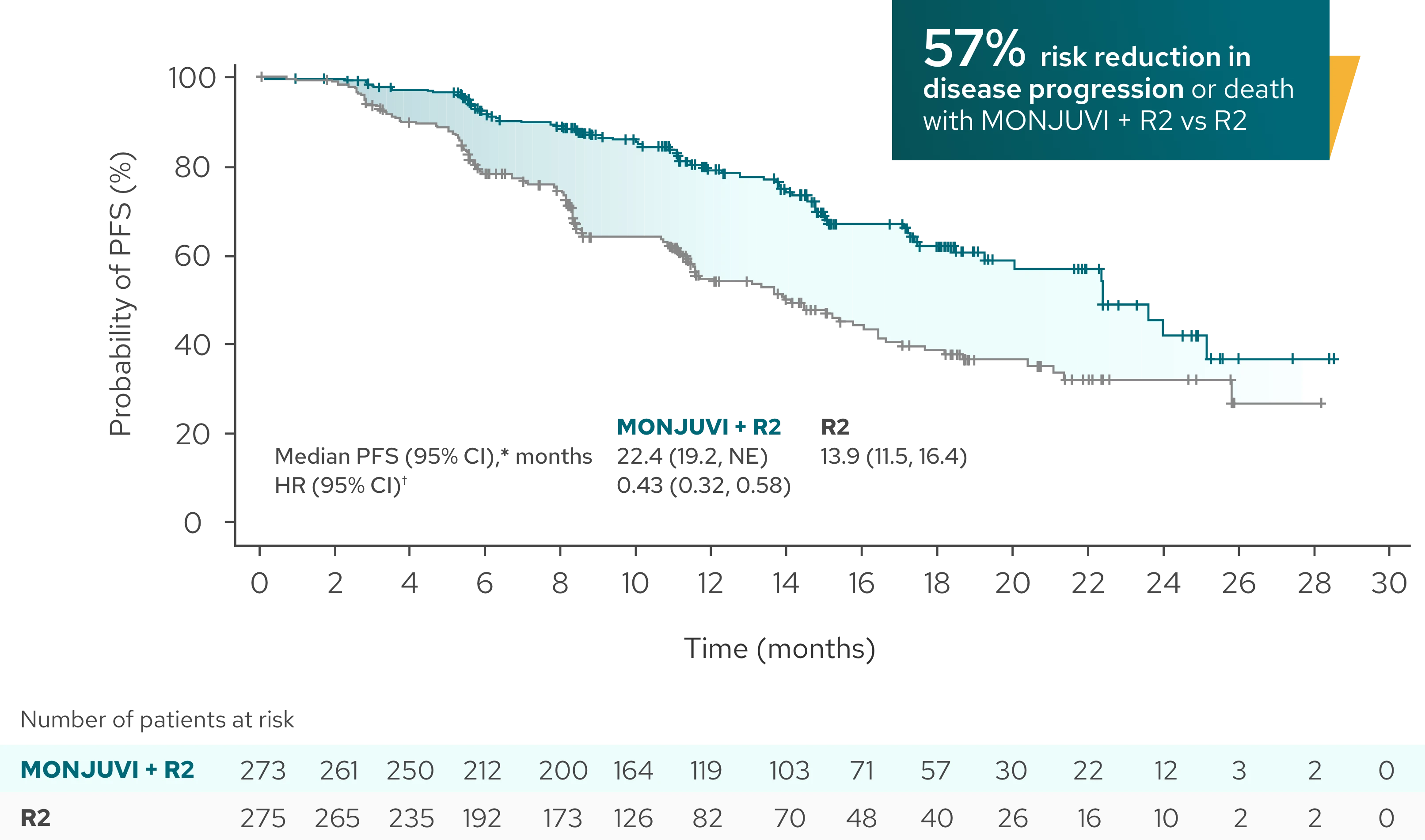
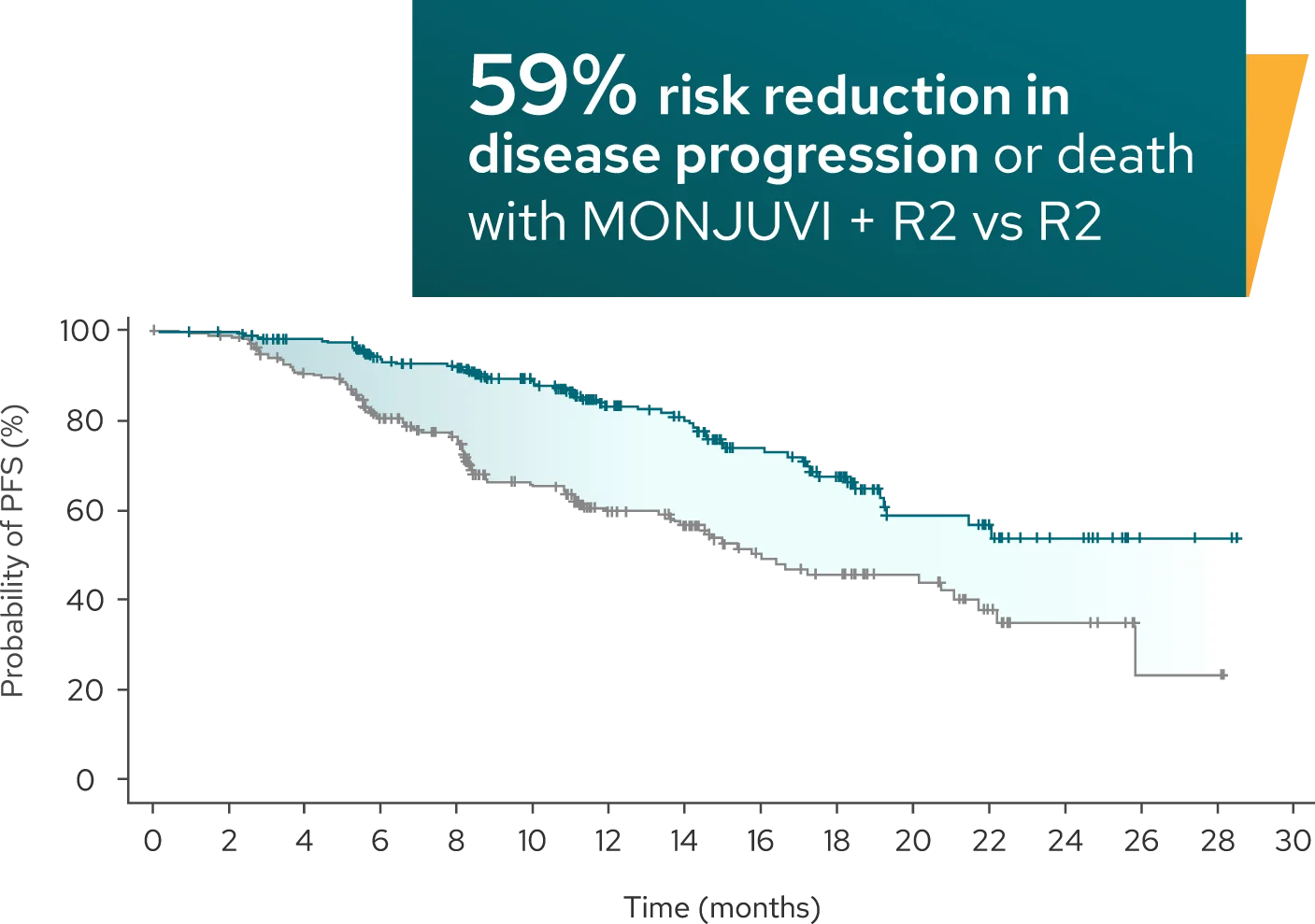
Superior efficacy: Significantly longer PFS demonstrated with MONJUVI + R2 vs R21
Median PFS* was 22.4 months (95% CI: 19.2, NE) with MONJUVI + R2 (n=273)
vs 13.9 months (95% CI: 11.5, 16.4) with R2 (n=275) (HR†=0.43 [95% CI: 0.32,
0.58]; P<0.0001) after a median follow-up of 14.1 months
Investigator-Assessed PFS (Primary Endpoint)
+
Tap to enlarge
| MONJUVI + R2 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Median PFS (95% CI),* months | 22.4 (19.2, NE) | 13.9 (11.5, 16.4) |
| HR (95% CI)† | 0.43 (0.32, 0.58) | |
| P-value | <0.0001 |
inMIND was a Phase 3, double-blind, international, multicenter study of 548 adult patients with relapsed or refractory FL Grade 1, 2, or 3a after at least 1 systemic therapy, including an anti-CD20 antibody. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive 12 cycles of MONJUVI + R2 or placebo + R2. The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed PFS using the Lugano criteria.1,2
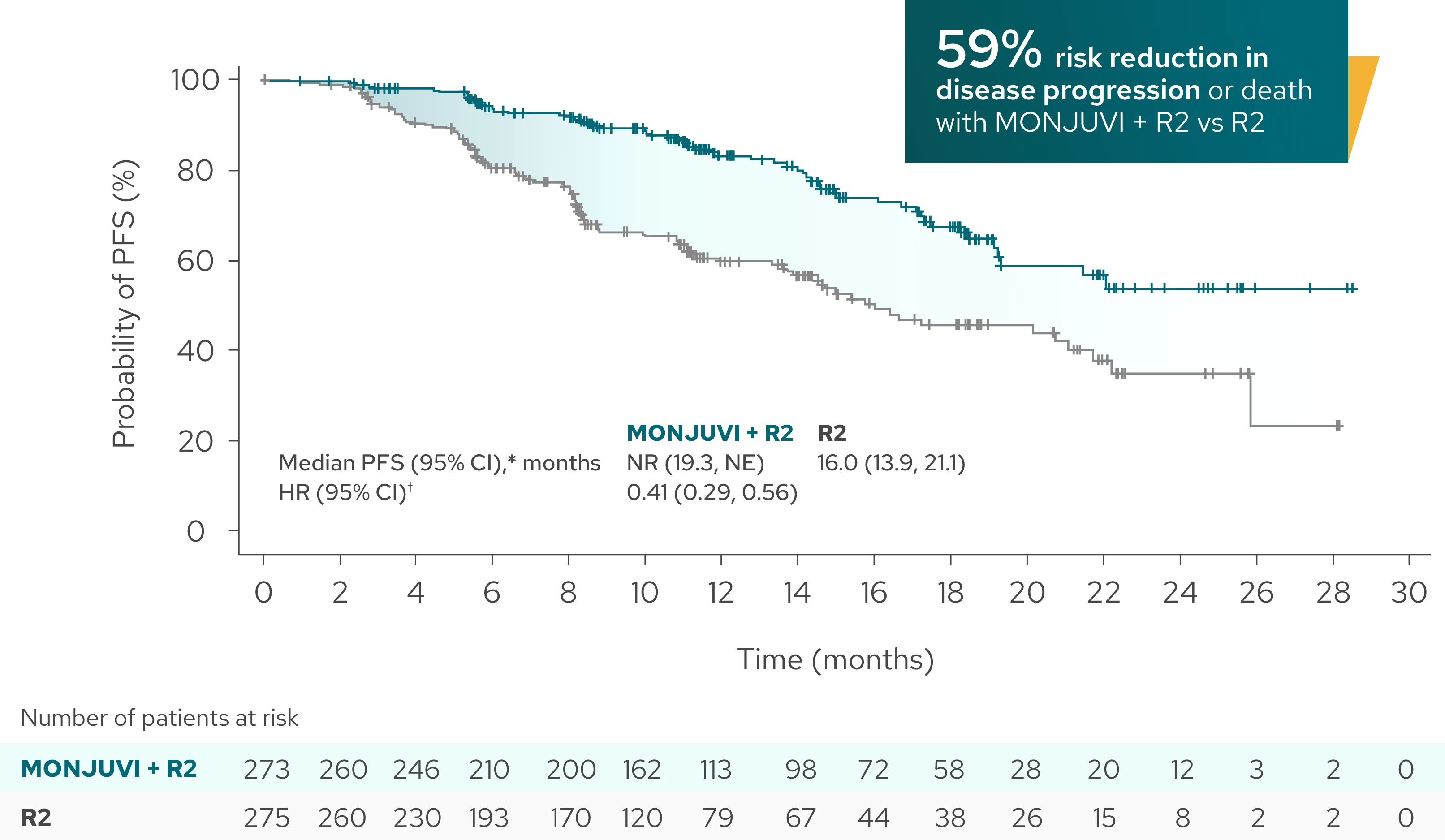
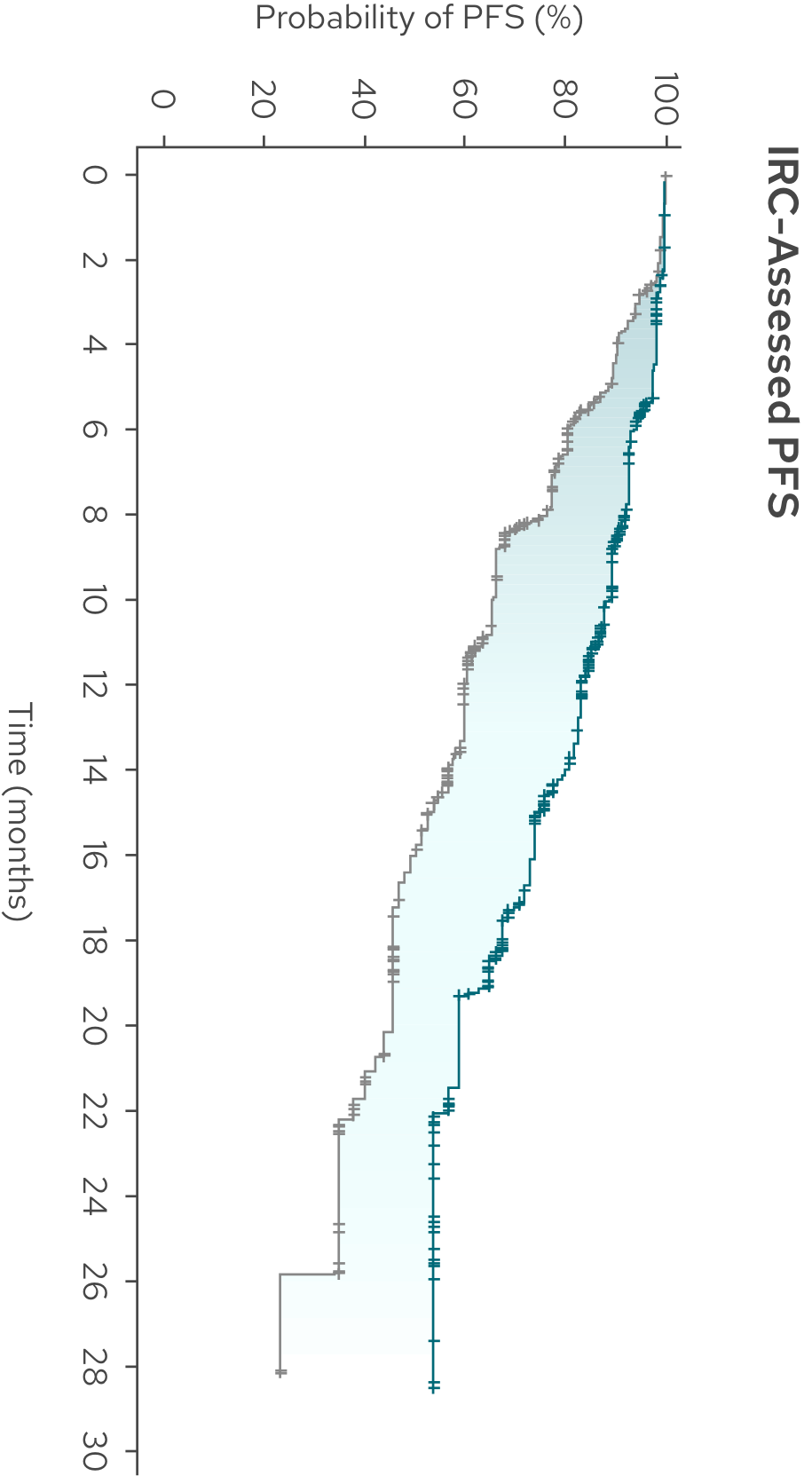
PFS benefit was consistent between the investigator assessment and IRC assessment1,3‡
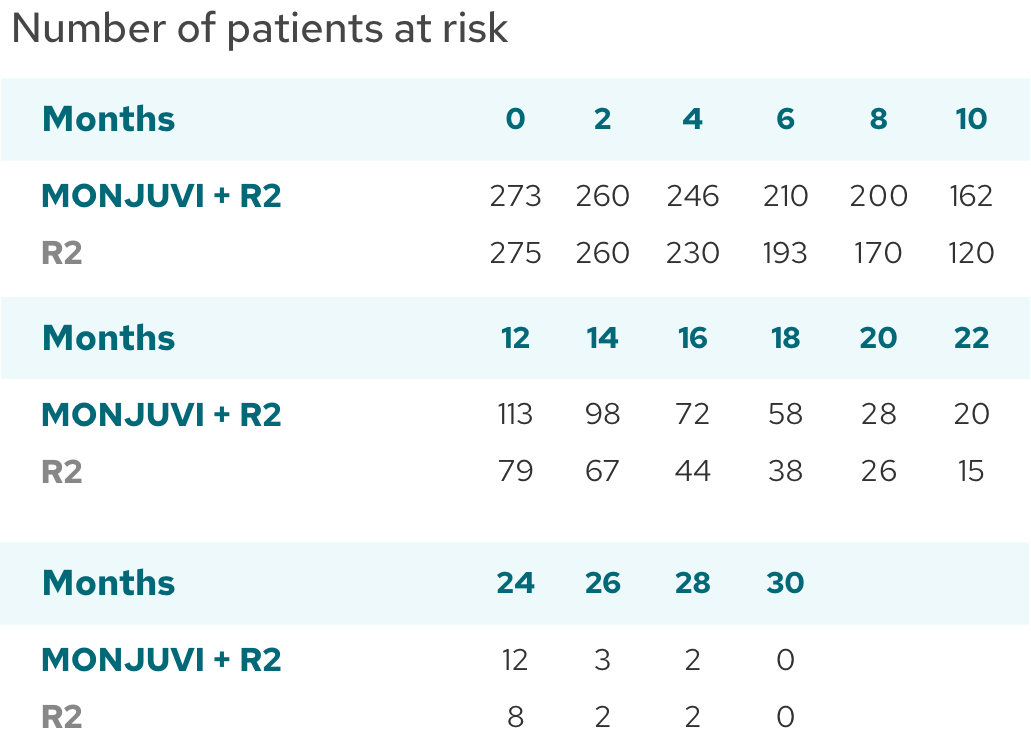
IRC-Assessed PFS (Secondary Endpoint)
Median PFS was not reached with MONJUVI + R2 vs 16 months with R23‡
+
Tap to enlarge
| MONJUVI + R2 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Median PFS (95% CI),* months | NR (19.3, NE) | 16.0 (13.9, 21.1) |
| HR (95% CI)† | 0.41 (0.29, 0.56) |
‡PFS by IRC assessment was not formally tested for statistical significance.
- ORR was 84% (95% CI: 79%, 88%) in the MONJUVI + R2 arm (n=228/273) vs 72% (95% CI: 67%, 78%) in the R2 arm (n=199/275)1
FL=follicular lymphoma; R2=rituximab and lenalidomide; PFS=progression-free survival; CI=confidence interval; NE=not evaluable; HR=hazard ratio; IRC=Independent Review Committee; NR=not reached; ORR=overall response rate.
*Kaplan-Meier estimates.1,3
†Hazard ratio based on a stratified Cox proportional hazards model.1,3
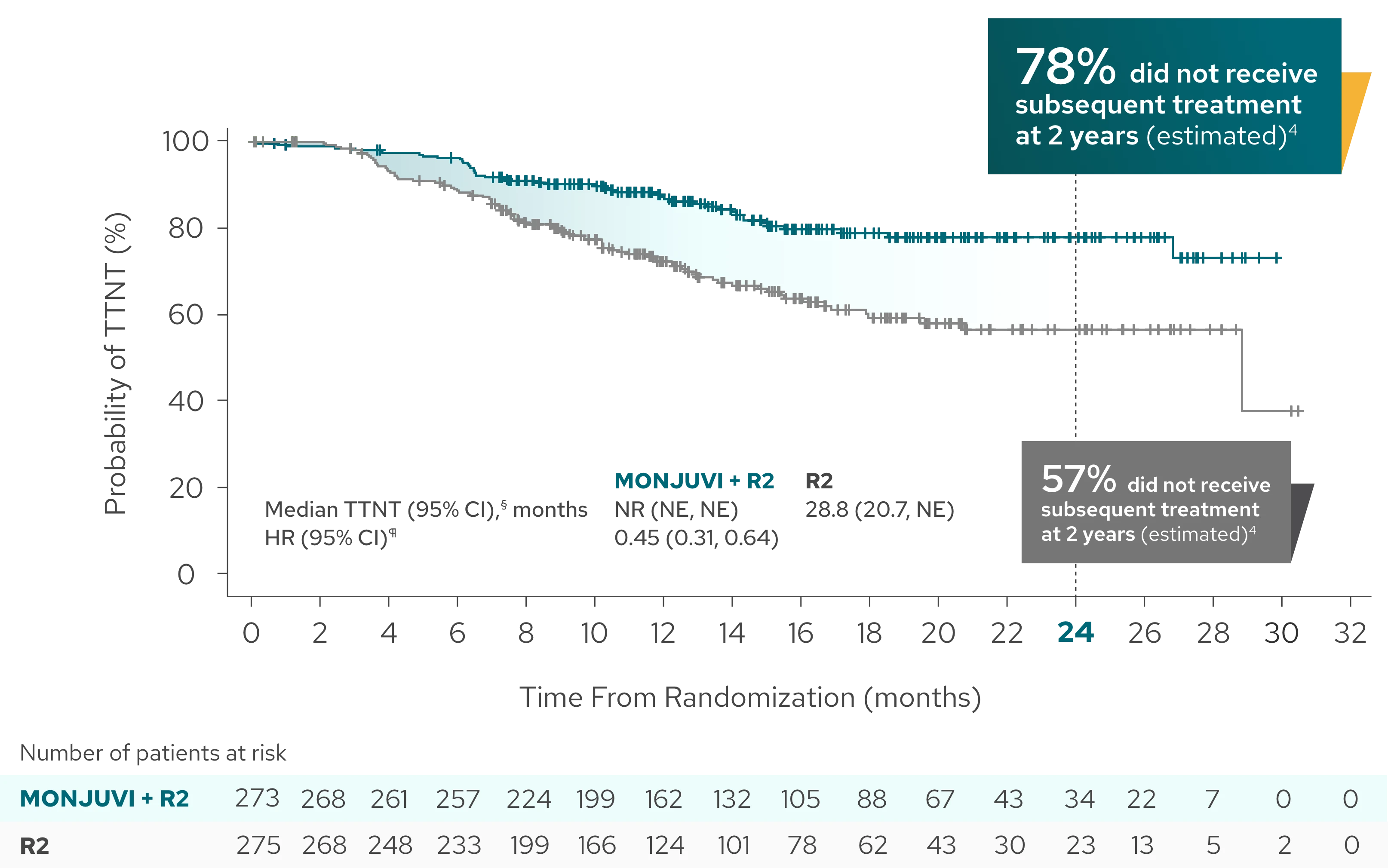
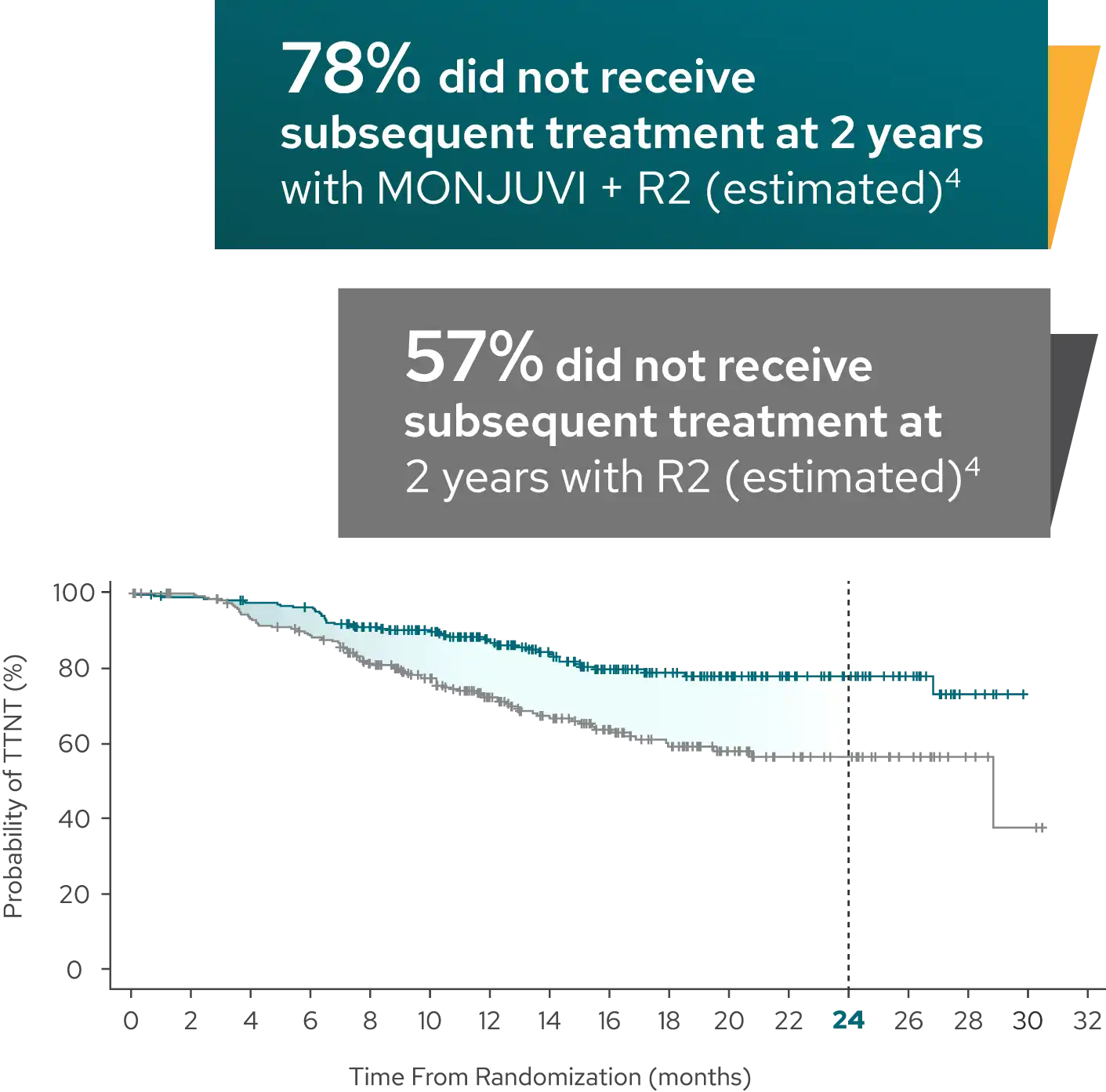
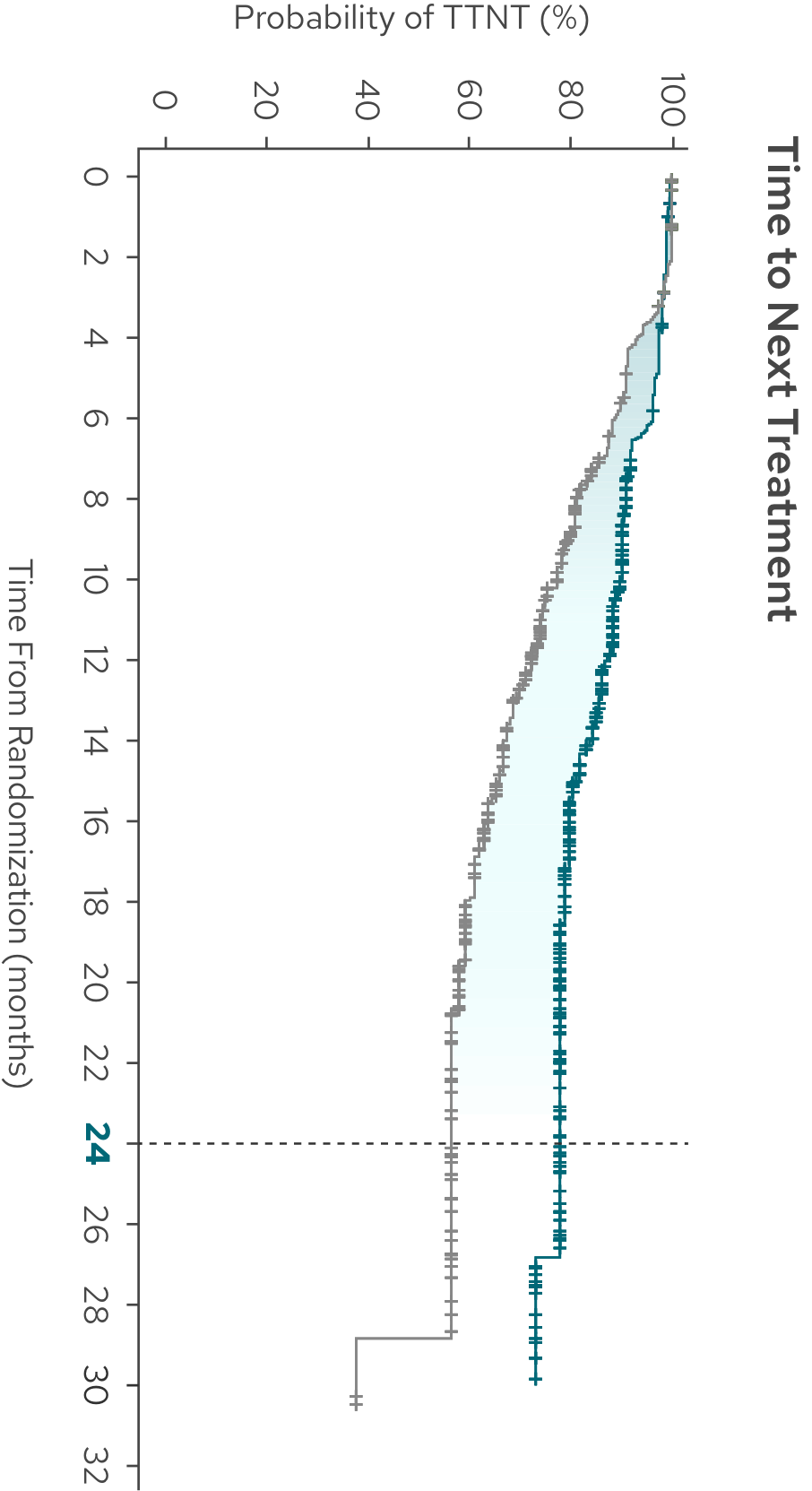
Median time to next treatment not reached with MONJUVI + R2 vs 28.8 months with R23
Exploratory Endpoint
+
Tap to enlarge
| MONJUVI + R2 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Median TTNT (95% CI),§ months | NR (NE, NE) | 28.8 (20.7, NE) |
| HR (95% CI)¶ | 0.45 (0.31, 0.64) |
Time to next treatment was defined as the time from randomization to start of next anti-lymphoma therapy for any reason or death due to any cause, whichever occurs first.4
Limitations of Analysis
The decision to initiate subsequent treatment was made by the treating physician and patient and is subject to variability based on investigator interpretation of patient and disease characteristics. The time to next treatment analysis is exploratory in nature and should be interpreted with caution.
§Kaplan-Meier estimates.3
¶Estimated using a stratified Cox proportional hazards model.3
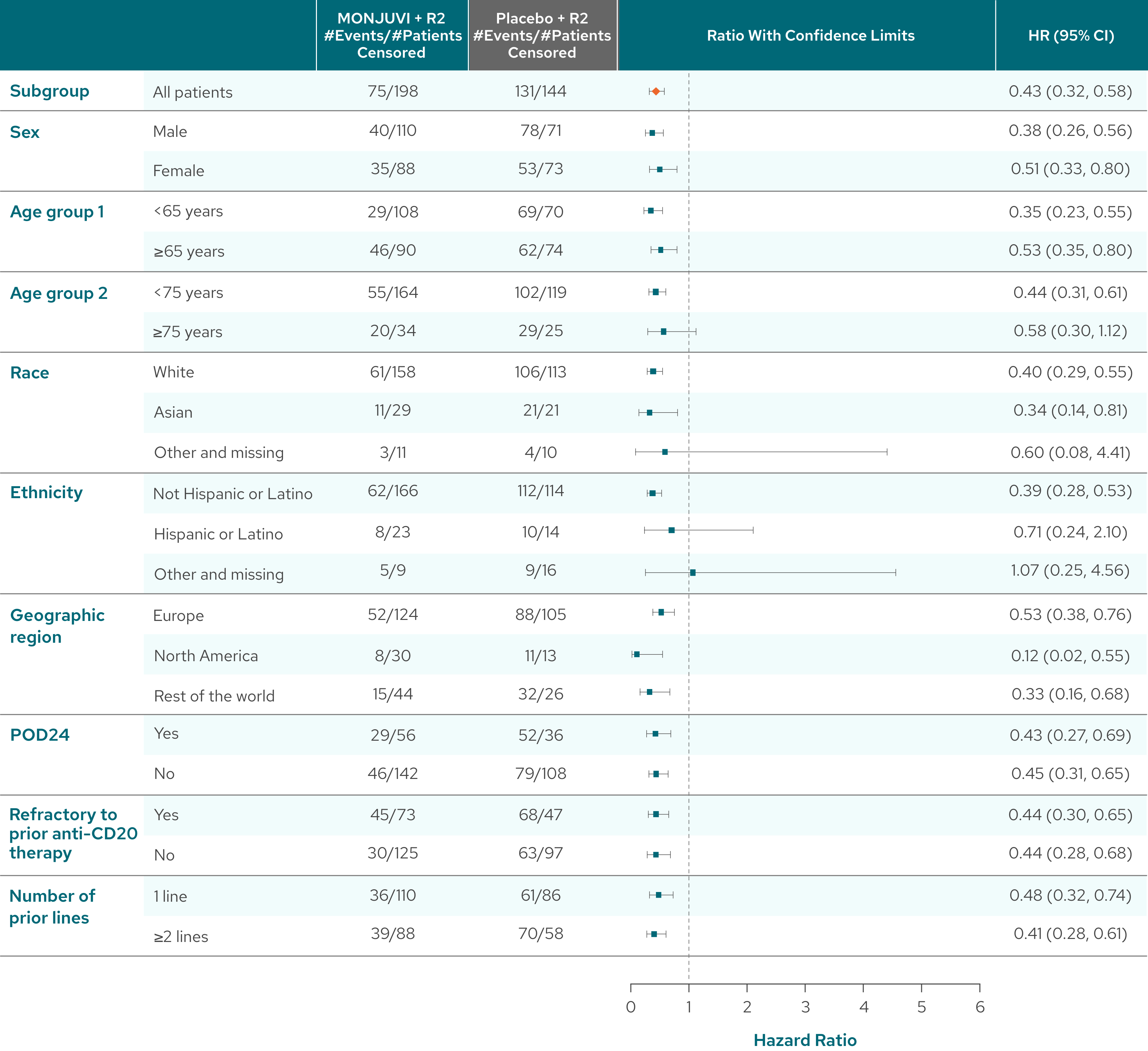
PFS benefit was consistent across patient subgroups with MONJUVI + R23#
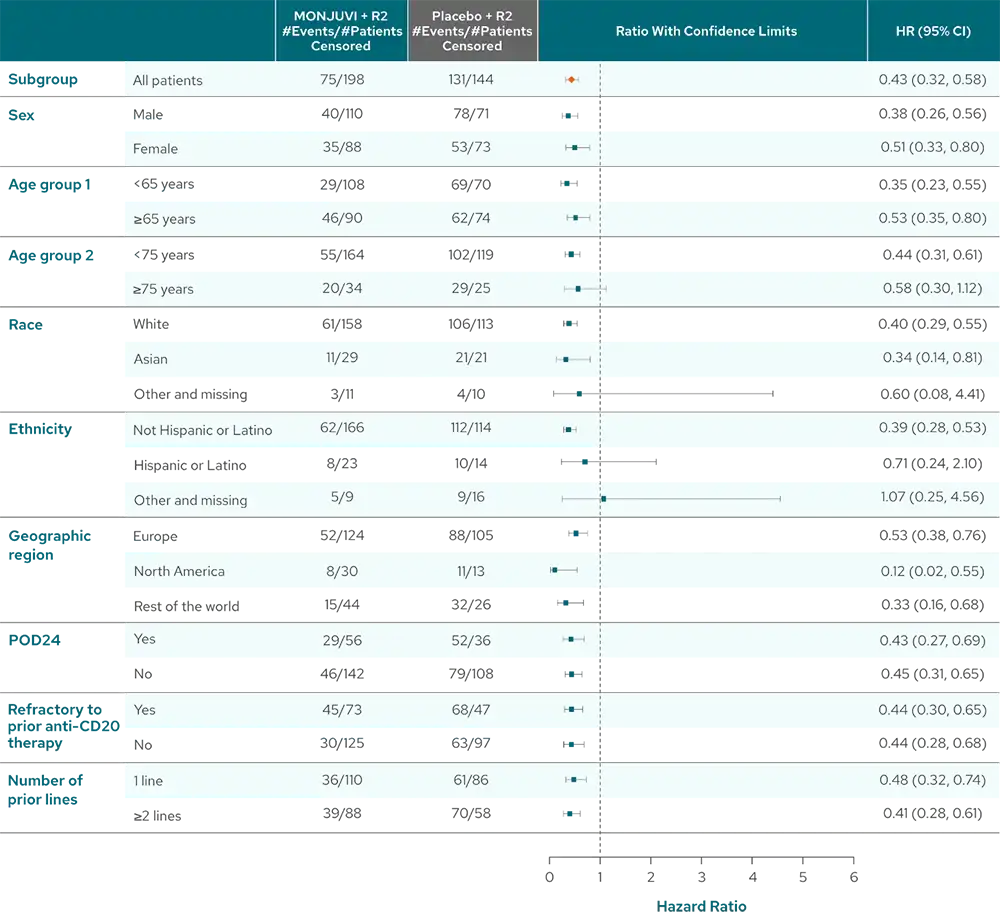
Pinch to zoom
- POD24 was defined as progression of disease within 24 months after initial diagnosis1
- Refractoriness to prior anti-CD20 therapy was defined as not achieving a CR or PR to a prior regimen containing anti-CD20 mAb, or disease progression occurring during treatment with, or relapse <6 months after last dose of anti-CD20 mAb.4
Limitations of Analysis
The subgroup analysis is exploratory in nature and inMIND was not designed or powered to evaluate and compare multiple subgroups. These results should be interpreted with caution.
#Analysis by investigator assessment.3
